Analysis by WorldTribune Staff, May 6, 2019
Two decades after Hugo Chavez vowed to lift up the poor and promised a better future for all, Venezuela’s once prosperous economy is in shambles, citizens pick through garbage looking for scraps of food, vital medicines are in short supply and more than 3 million people have fled the socialist destination of Chavez’s policies.
Chavez’s handpicked successor, dictator Nicolas Maduro, is locking up store owners and opposition leaders, drawing angry protesters into the streets. The death toll increased again last week when a 14-year-old boy was shot in the head, reportedly by police. Maduro is even slapping sanctions on U.S. politicians that criticize the repression.
 The socialist country’s inflation rate is expected to hit 10 million percent in 2019.
The socialist country’s inflation rate is expected to hit 10 million percent in 2019.
U.S. conservative commentator Larry Ward noted in a May 4 Facebook post (see graphic at left): “Democratic Socialism lifecycle. Now you dangerous crazy liberals who want this for America, save some time and move to Venezuela, and STFU about capitalism and guns.”
Related: Many in Venezuela now regret ban on private citizen gun ownership, May 1, 2019
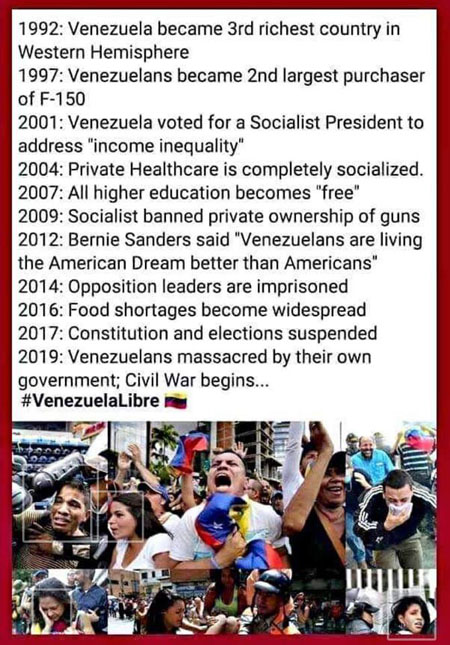
Public Radio International (PRI.org) put together a timeline recording the descent of Chavez’s “Bolivarian” socialist revolution into repression and economic disaster:
February 1992
Paratroop Lt. Col. Hugo Chavez bursts onto the scene when he leads a failed coup against an elected government that had overseen the bloody repression of street protests against a gasoline price hike. Chavez is jailed — but not forgotten by many grateful Venezuelans.
March 1994
Chavez is freed. President Rafael Caldera dismisses the charges but discharges Chavez and other mutinous officers from the military.
December 1998
Chavez is elected president. He promises a “third way” between capitalism and socialism.
July 1999
Chavez supporters win 122 of 128 seats in a constituent assembly, allowing the president to rewrite the constitution. He eliminates the senate, lengthens the presidential term from five to six years, and renames the country the “Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela” after his idol Simon Bolivar, the inspiration behind most of Latin America’s independence from Spain.
April 2002
Chavez is briefly taken prisoner during a failed coup led by business leaders and dissident generals. President George W. Bush’s White House swiftly publicly backs the coup plotters — only to end up badly wrong-footed when Chavez triumphantly returns to office. It comes less than two years after he is re-elected under the new constitution and in response to anti-Chavez protests that ended in gunfire.
December 2002
Unions, business leaders, political parties and thousands of workers at state oil company PDVSA strike to demand an immediate referendum on whether Chavez should leave office. It peters out after two months.
April 2003
Chavez stamps his authority on PDVSA by firing seven senior executives and 18,000 workers for participating in the strike.
August 2004
In a referendum, Venezuelans vote overwhelmingly against making Chavez leave office immediately.
December 2004
Chavez and Cuba’s Fidel Castro sign a cooperation agreement that eventually gives birth to the Bolivarian Alliance of the Americas, or ALBA, a bloc of largely leftist, anti-Washington governments including Bolivia, Ecuador and Nicaragua.
September 2006
Chavez’s most famous moment comes as he gives a speech to the United Nations General Assembly, in which he calls George W. Bush “the devil.” With much of Latin America appalled by the U.S.-led invasion of Iraq, the comment sparks mirth, and even toasts, around the world.
December 2006
Chavez wins re-election to his second six-year term. Now at the height of his powers, the president talks openly about his grandiose plans to unify Latin America.
January 2007
The national assembly gives Chavez sweeping powers to rule by decree. With the price of oil, which accounts for most of Venezuela’s exports, heading up to $100 a barrel, Chavez lavishes cash on anti-poverty programs like never before. Critics warn the spree is unsustainable.
May 2007
Venezuela’s oldest TV station, Radio Caracas Television, a longtime Chavez critic, falls silent after the government decides against renewing its broadcast license. The move marks the start of a policy of systematically squeezing out of business, or taking over, media outlets that question the government.
September 2008
Chavez boots out the U.S. ambassador, accusing him of plotting against the government. That same month, he also expels independent researchers from Human Rights Watch, in a portent of the abuses that his government and that of his successor, Nicolas Maduro, would increasingly commit.
February 2009
Voters approve an end to term limits, paving the way for Chavez to rule indefinitely.
June 2011
Chavez heads to Cuba for surgery to remove an abscess from his pelvis. Three weeks later he confirms on TV that the tumor was cancerous.
September 2011
The president says he has successfully completed a course of chemotherapy.
October 2011
On hearing of Col. Moammar Gadhafi’s death, Chavez describes the brutal Libyan dictator as a “liberator” and “martyr.”
February 2012
Chavez reveals doctors have told him the cancer has returned.
October 2012
Chavez wins re-election again, three months after declaring himself “totally free” of cancer — to the skepticism of some of his critics.
December 2012
The president announces that his cancer has returned. In the same TV address, he names his Vice President Nicolas Maduro, a former bus driver and union leader, as his political heir. This is the last time Chavez is seen in public. Two days later he undergoes major surgery in Cuba.
March 2013
Officials announce Chavez’s death. To this day, they have yet to reveal the type of cancer that killed him. Maduro is sworn in as interim president, pending elections. Mourners at the funeral include longtime Chavez ally Mahmoud Ahmadinejad, then the Iranian president, who kisses the coffin.
April 2013
Maduro narrowly beats opposition leader Henrique Capriles, by less than 2 percentage points, following a ferocious presidential campaign. Critics claim the new president took the Chavez tactic of using state resources, especially TV airtime, to new heights. Amid opposition complaints of vote-rigging, the National Electoral Council vows a full audit of the result “to preserve a climate of harmony between Venezuelans.” It never fulfills that promise.
September 2013
As the economy wobbles, Maduro expels three U.S. diplomats for supposedly orchestrating a massive power outage. “Yankee go home,” he declares on TV. “Enough abuses already.”
February 2014
Student demonstrations against violent crime quickly morph into national anti-government protests. Dozens die in clashes with security forces during the demonstrations. One opposition leader, Leopoldo Lopez, leads the charge, calling for peaceful marches to bring about the “salida” or “exit” of the government. He is arrested for allegedly orchestrating a coup and, one year later, remains behind bars. His arrest is the first of several of prominent dissidents, including two provincial mayors.
April 2014
The United Nations publishes its 2013 homicide report, which confirms what long-suffering Venezuelans already know: after 15 years of Chavismo, their country is so ultra-violent it is not safe to leave home even in broad daylight. According to the numbers, Venezuela is the world’s second most murderous nation.
September 2014
With inflation at 60 percent and oil prices plummeting, Maduro warns he will take unspecified “actions” against a Harvard professor who suggests Caracas might default on its national debt.
November 2014
Despite having recently been declared by OPEC, the oil exporting nations’ club, as the country with the largest oil reserves — larger even than Saudi Arabia’s — Venezuela is reported to be importing crude. After 15 years of “socialist” Chavista economics, this may be the most telling sign of the shambles the country is in.
December 2014
President Barack Obama signs a law that punishes Venezuelan government officials, freezing their U.S. assets and denying them visas.
January 2015
Official inflation reaches 64 percent. The government bans desperate shoppers from lining up overnight at supermarkets.
February 2015
The government devalues the bolivar by 69 percent. In a televised speech on the same day, Maduro completely omits the bombshell and instead alleges that the U.S. was on the point of sending fighter jets to bomb his presidential palace. He also approves new rules that, Human Rights Watch says, authorize the military to fire on peaceful protests. One week later, Caracas’ opposition mayor Antonio Ledezma, a vocal critic of the government but not someone viewed as either a likely presidential rival or insurgency leader, is arrested. On Feb. 28, Maduro announces limits on the number of U.S. diplomats in Venezuela and new visa requirements for American visitors. He also says he will deny visas to George W. Bush, Marco Rubio and other U.S. politicians, calling them “terrorists.”
Your Intel Brief: Geostrategy-Direct __________ Fix The Media Now
